We use the glmer function from package lme4 in order to fit the model. The nAGQ argument controls the number of nodes in the quadrature formula.
Generalized Linear Mixed Models In Ecology And In R R Bloggers
GlmmTMB is an R package built on the Template Model Builder automatic di erentiation engine for tting generalized linear mixed models and exten-sions.
. For a GLMM the integral must be approximated. R programming GLM in R. The most reliable approximation for GLMMs is adaptive Gauss-Hermite quadrature at present implemented only for models with a single scalar random effect.
We can check the model using the function summary. You probably learned how to calculate confidence intervals and conduct hypothesis tests on regression coefficients. I am trying to run a Generalized linear mixed model GLMM on r I have two fixed factors and two random factors however there are a lot of holes in my data set and the I am struggling to find a code to run the glmm all I found is the glm Can someone please walk me through this I know very little about R and coding.
The general form of the model in matrix notation is. Generalized Linear Mixed Model Tutorial in R. X is a N p matrix of the p predictor variables.
A vector of the Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates. R square computation for GLMM see supplementary material from Nakagawa 2013 MEE VarF. Lets move on to R and apply our current understanding of the linear mixed effects model.
Mixed models in R For a start we need to install the R package lme4 Bates Maechler Bolker 2012. Glmm returns an object of class glmm is a list containing at least the following components. Y X β Z u ε.
Not-yet-implemented features are denoted like this response distributions. A GLMM gives you all the advantages of a logistic regression model1 Handles a multinomial response variable. Import the data into R.
The glimmix procedure fits these models. Where y is a N 1 column vector the outcome variable. GLMM and R issues.
Sal. A model with a single scalar random-effects term could reasonably use. Gaussian binomial beta-binomial Poisson negative binomial NB1 and NB2 parameterizations Conway-Maxwell-.
D. A model with a single scalar random-effects term could reasonably use. For a GLMM the integral must be approximated.
These are worked examples for a book chapter on mixed models in Ecological Statistics. Whether you knew it or not these sorts of statistical inference for the linear model usually rely on three requirements. This tutorial follows this structure.
December 4 2010 Daniel Hocking. Contribute to francojraglmm_tutorial development by creating an account on GitHub. It isnt designed to teach you about hardcore Bayesian statistics or mixed modelling but rather to highlight the differences between.
The most current take on this material can be found in Richards textbook of the. Generalized Linear Model Generalized linear model GLM is a generalization of ordinary linear regression that allows for response variables that have error distribution models other than a normal distribution like Gaussian distribution. The general content of the tutorial was inspired by Richard McElreaths excellent statistics course Statistical Rethinking.
Basics of GLM GLMs are fit with function glm. GLMM is the general model with LM LMM and GLM being special cases of. While being connected to the internet open R and type in.
Jarrod Hadfield to help you become comfortable with using the package and learn some of the ways you can analyse your data. Furthermore the tutorial briefly demonstrates the multilevel extension of GLM models with the lme4 package in R. Lets have a closer look at the syntax.
Strd Convert Study to a factor as opposed to an integer variable d Study. β is a p 1 column vector of the fixed. The residuals are normally distributed the.
Generalized linear mixed models GLMM are for normal or non-normal data and can model random and or repeated effects. A vector of the Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates MCMLEs for the fixed effects. Alternatively you could think of GLMMs as an extension of generalized linear models eg logistic regression to include both fixed and random effects hence mixed models.
Think back to intro stats when you learned to perform linear regression. The nAGQ argument controls the number of nodes in the quadrature formula. Lastly more distributions and link functions in the GLM framework are discussed.
The most reliable approximation for GLMMs is adaptive Gauss-Hermite quadrature at present implemented only for models with a single scalar random effect. I have been trying to run a Generalized Linear Mixed Model GLMM for some count data with repeated measures on sub-sampled sites and fixed effects at the site level with covariates at. Generalized Linear Mixed Models.
This repository contains a relatively brief tutorial on generalized linear mixed models GLMMs using R to fit and compare models. This tutorial is aimed at people who are new to meta-analysis and using the MCMCglmm package written by Dr. Mod1 glmerformula cbindLonger Total - Longer X 1 Subject family binomiallink probit data datafr summarymod1 The fitted model is named as mod1.
Handles unbalanced data Gives more information on the size and direction of effects Has an explicit model structure adaptable post hoc for different analyses rather than re-quiring different experimental designs.

Glm In R Generalized Linear Model With Example

Glm In R Generalized Linear Model With Example
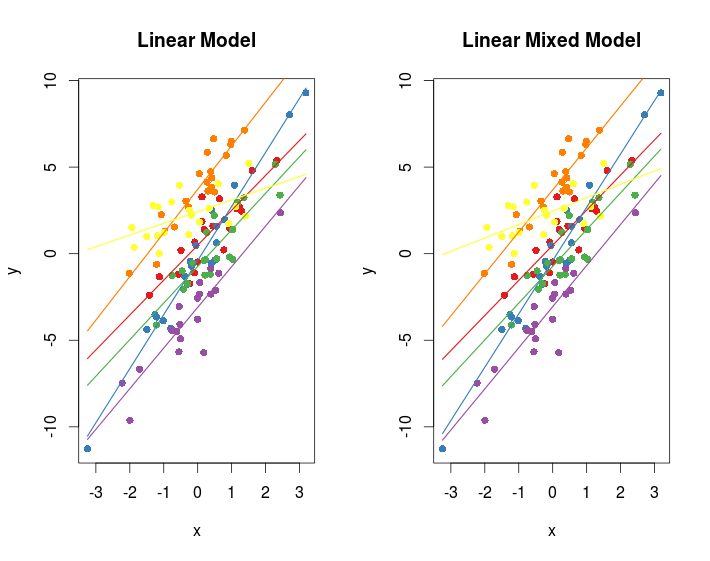
Generalized Linear Mixed Models In Ecology And In R Biologyforfun
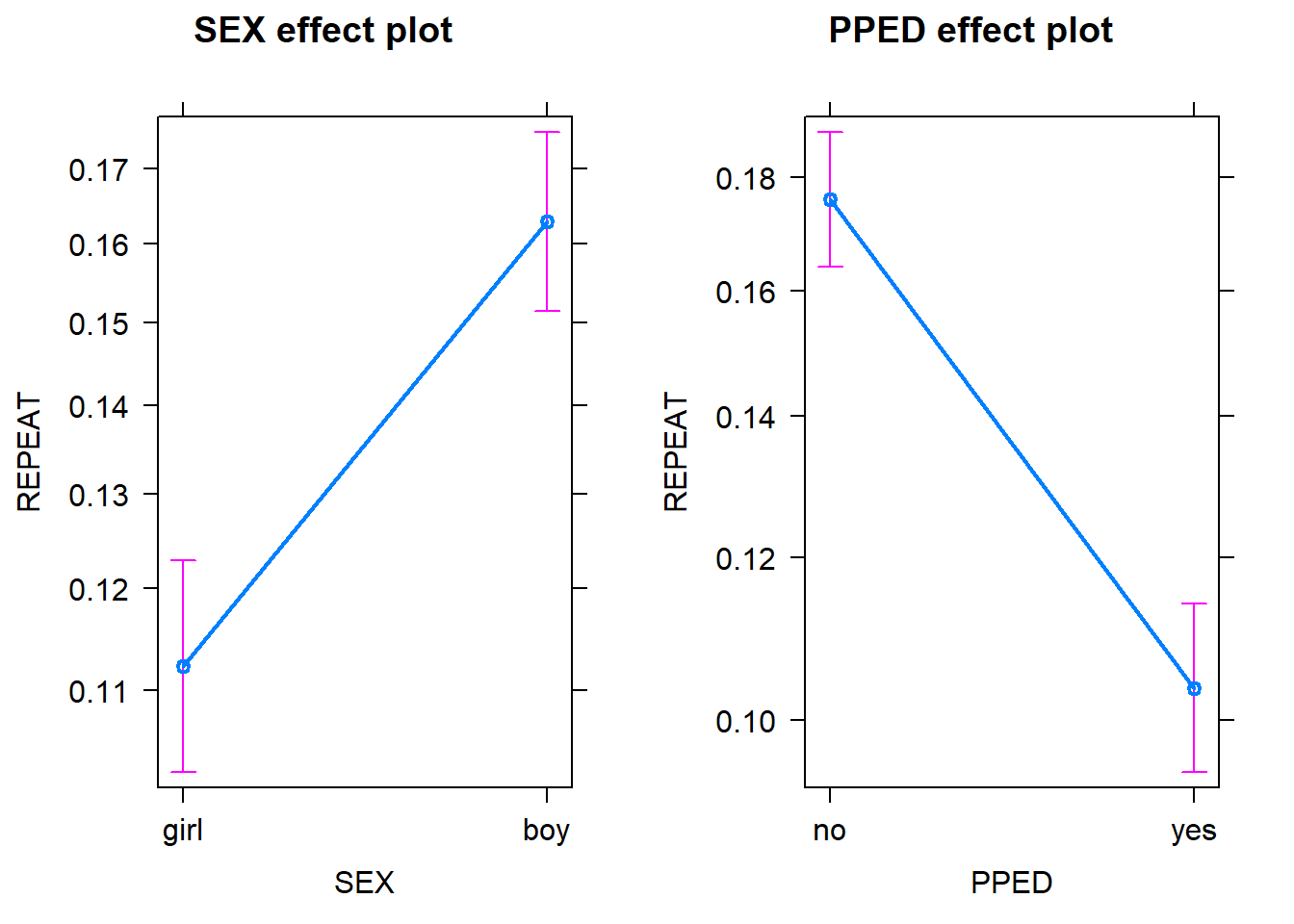
Generalised Linear Models With Glm And Lme4 Rens Van De Schoot
Generalized Linear Mixed Models In Ecology And In R R Bloggers
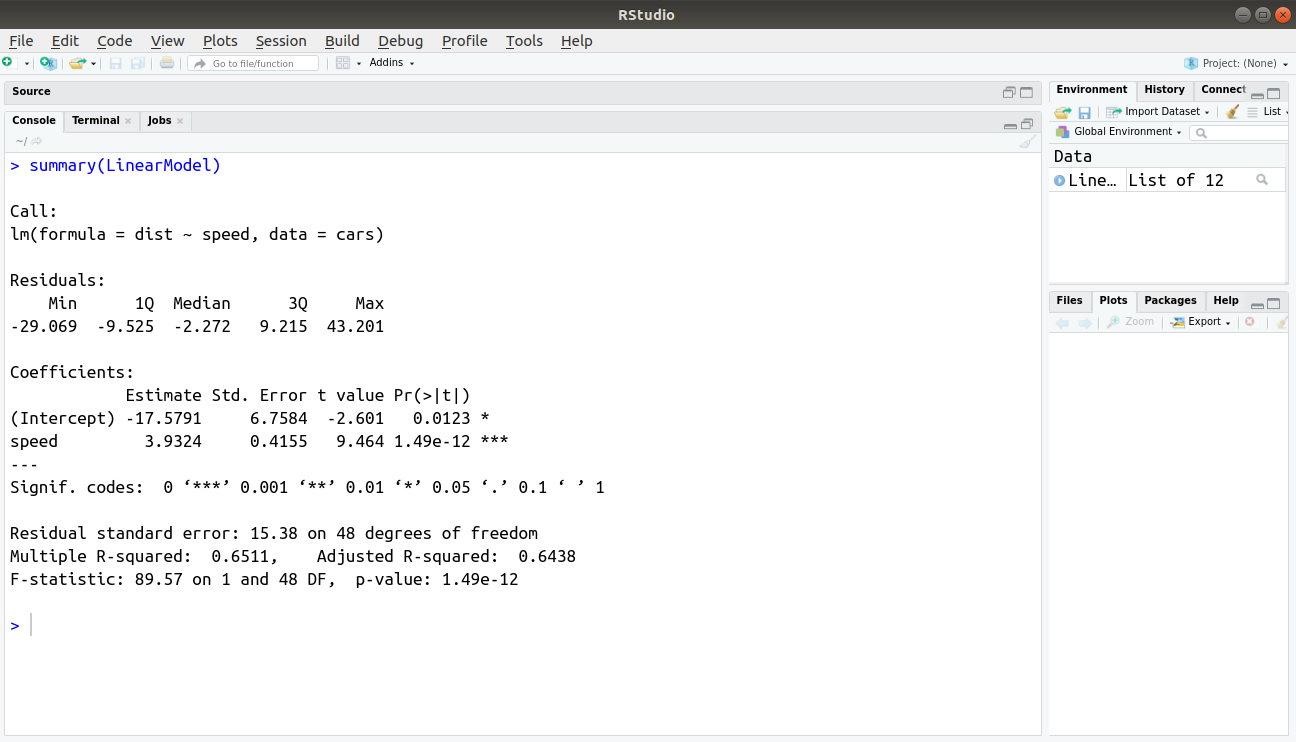
How To Create Generalized Linear Models In R The Expert S Way Dataflair
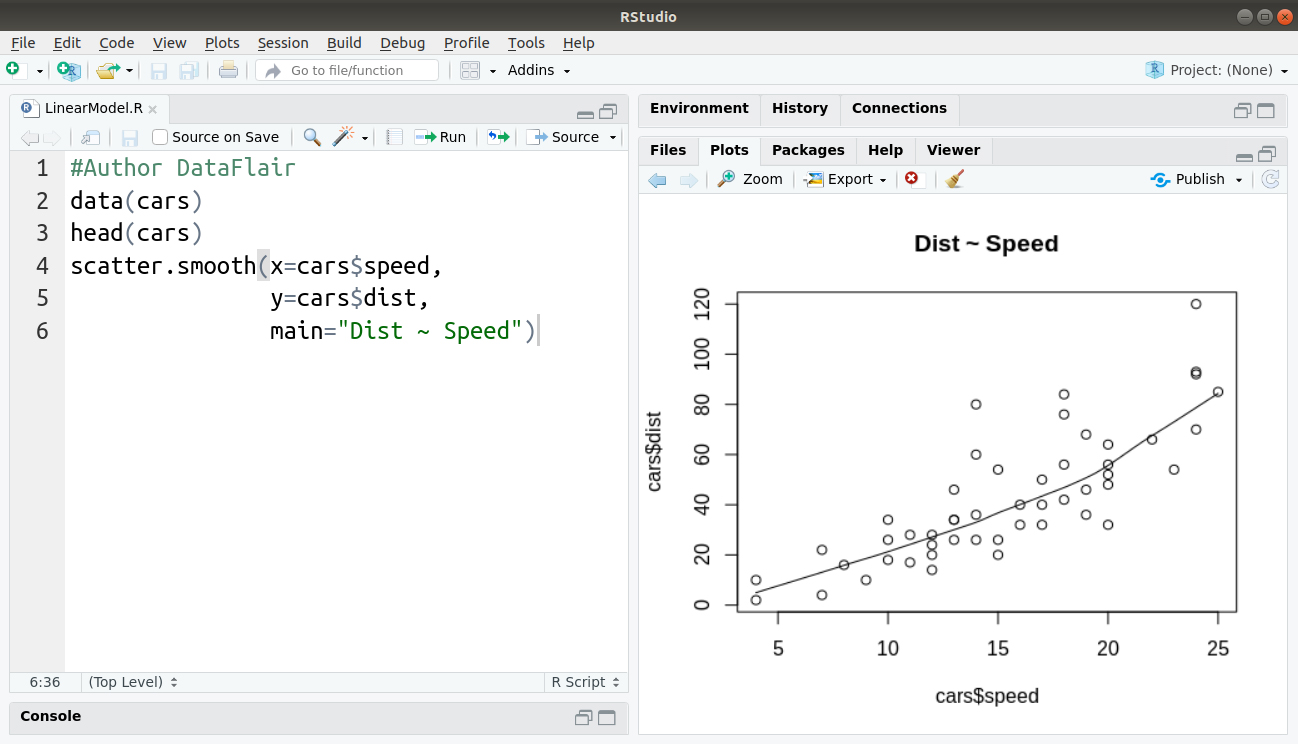
How To Create Generalized Linear Models In R The Expert S Way Dataflair
0 comments
Post a Comment